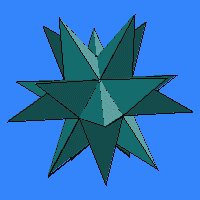
 In
the great stellated dodecahedron
and the small stellated
dodecahedron, the faces are pentagrams.
It is easier to see which parts of the exterior belong to which pentagram
if you look at a six-colored
model of the great stellated dodecahedron and a six-colored
model of the small stellated dodecahedron. The center of each
pentagram is hidden inside the polyhedron. These two polyhedra were described
by Johannes Kepler in 1619, and he deserves credit
for first understanding them mathematically, but a 16th century drawing
by Jamnitzer is very similar to the former
and a 15th century mosaic attributed to Uccello
illustrates the latter.
In
the great stellated dodecahedron
and the small stellated
dodecahedron, the faces are pentagrams.
It is easier to see which parts of the exterior belong to which pentagram
if you look at a six-colored
model of the great stellated dodecahedron and a six-colored
model of the small stellated dodecahedron. The center of each
pentagram is hidden inside the polyhedron. These two polyhedra were described
by Johannes Kepler in 1619, and he deserves credit
for first understanding them mathematically, but a 16th century drawing
by Jamnitzer is very similar to the former
and a 15th century mosaic attributed to Uccello
illustrates the latter.
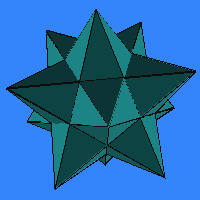 These
two polyhedra have three and five pentagrams, respectively, meeting at
each vertex. Because the faces intersect each other, parts of each face
are hidden by other faces, and you need to see
that the visible portions of the faces are not the complete faces.
These
two polyhedra have three and five pentagrams, respectively, meeting at
each vertex. Because the faces intersect each other, parts of each face
are hidden by other faces, and you need to see
that the visible portions of the faces are not the complete faces.
 In
the great icosahedron and great
dodecahedron (described by Louis Poinsot in 1809, although Jamnitzer
made a picture of the great dodecahedron in 1568) the faces (20 triangles
and 12 pentagons, respectively) which meet at each vertex "go around twice"
and intersect each other, in a manner which is the 3D analog to what happens
in 2D with a pentagram.
In
the great icosahedron and great
dodecahedron (described by Louis Poinsot in 1809, although Jamnitzer
made a picture of the great dodecahedron in 1568) the faces (20 triangles
and 12 pentagons, respectively) which meet at each vertex "go around twice"
and intersect each other, in a manner which is the 3D analog to what happens
in 2D with a pentagram.
 If
you slice the polyhedron near a vertex, you'll see a pentagram cross section
as the vertex figure. For example, this cutaway
view of the great dodecahedron shows how the five pentagons which meet
at a vertex pass through each other in the manner of a pentagram. Study
the virtual models to see this. To emphasize that these polyhedra are made
of large convex faces, it helps to look at a five-color
model of the great icosahedron and a six-color
model of the great dodecahedron.
If
you slice the polyhedron near a vertex, you'll see a pentagram cross section
as the vertex figure. For example, this cutaway
view of the great dodecahedron shows how the five pentagons which meet
at a vertex pass through each other in the manner of a pentagram. Study
the virtual models to see this. To emphasize that these polyhedra are made
of large convex faces, it helps to look at a five-color
model of the great icosahedron and a six-color
model of the great dodecahedron.
Together, the Platonic solids and these Kepler-Poinsot polyhedra form the set of 9 regular polyhedra. Cauchy first proved that no other polyhedra can exist with identical regular faces and identical regular vertices.
Here are some relationships you should observe:
- The great dodecahedron has the same vertices and edges as the icosahedron.
- The small stellated dodecahedron has the same vertices and edges as the great icosahedron. These both have the same vertices (but not edges) as the icosahedron.
- The great stellated dodecahedron has the same vertices (but not edges) as the dodecahedron.
- All four have the same symmetry axes and symmetry planes as the icosahedron and dodecahedron.
Exercise: Which of these four polyhedra have a dodecahedron and which an icosahedron as their innermost region? Imagine how the planes intersect, then travel inside to find out. (Note: be sure to find the centermost region.)
Answer: Find out when you read about stellations.
If you are considering making paper models of these polyhedra, be sure to consider a number of nice colorings which are possible.